T-test
T-test
A t-test is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t distribution if the null hypothesis is supported. It can be used to determine if two sets of data are significantly different from each other, and is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution.
Among the most frequently used t-tests are:
- A one-sample location test of whether the mean of a population has a value specified in a null hypothesis.
- A two-sample location test of the null hypothesis that the means of two populations are equal. All such tests are usually called Student's t-tests, though strictly speaking that name should only be used if the variances of the two populations are also assumed to be equal; the form of the test used when this assumption is dropped is sometimes called Welch's t-test. These tests are often referred to as "unpaired" or "independent samples" t-tests, as they are typically applied when the statistical units underlying the two samples being compared are non-overlapping.
- A test of the null hypothesis that the difference between two responses measured on the same statistical unit has a mean value of zero. For example, suppose we measure the size of a cancer patient's tumor before and after a treatment. If the treatment is effective, we expect the tumor size for many of the patients to be smaller following the treatment. This is often referred to as the "paired" or "repeated measures" t-test:
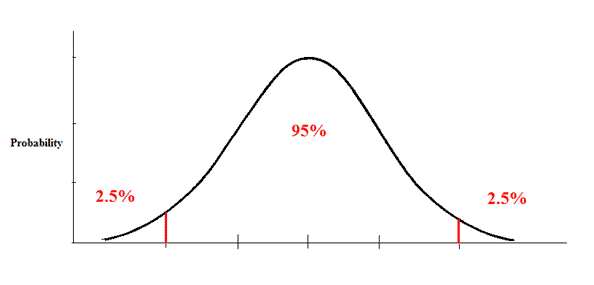
Generally for IPRO calculations on measures, the T-test is conducted using a normal distribution and a 95% confidence interval. Standard deviation is used to find the confidence interval, which is located plus/minus 1.96 standard deviations away from the value. In a normal distribution, at 1.96 standard deviations, 5% of the values exist above 1.96std_dev and 5% of the values exist below 1.96std_dev. The national or state average is compared to the calculated confidence interval tail for each value to determine if the value is significantly better or worse than that national or state average.
Measures that use the T-test calculation method are:
- Process of Care Measures (CMS)
- Readmissions/Mortality Measures (CMS)
- IQI, PSI, PDI, and PQI indicators (AHRQ Methodology)
- Infections Data
, multiple selections available,
Related content
Statistical Significance
Statistical Significance
More like this
Measures by Data Type
Measures by Data Type
More like this
Population Measures
Population Measures
More like this
Average Length of Stay Measures
Average Length of Stay Measures
More like this
Interquartile Range
Interquartile Range
More like this